Startup funding rounds are stages of financing that startups go through to raise capital to support their growth and development. These rounds are typically associated with specific milestones and objectives that the company aims to achieve. Each round involves the issuance of equity (ownership shares) in exchange for investment from various types of investors, including angel investors, venture capitalists, and sometimes, corporate investors.
Pre-Seed Round: The Pre-Seed round is the earliest stage of funding in a startup's journey. It is focused on validating the initial idea, conducting concept exploration, and performing market research. Funding amounts are relatively small, and investors often include friends, family, and occasionally, angel investors.
Seed Round: The Seed round comes after Pre-Seed and is aimed at validating the startup's concept further, building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), and gaining initial traction in the market. Funding is used for product development, initial marketing efforts, and team expansion. Investors may include angel investors and early-stage venture capital firms.
Series A Round: The Series A round is the next stage and is focused on accelerating the startup's growth. It typically follows successful market validation and aims to scale the business. Funding amounts are larger than Seed rounds and are used for marketing expansion, team growth, infrastructure enhancement, and preparing for further scaling. Investors often include established venture capital firms and institutional investors.
Series B Round: The Series B round is all about expanding and scaling the startup's operations. It comes after Series A and involves larger funding amounts. The funding is used for scaling existing products or services, market expansion, potential acquisitions, and solidifying the startup's position in the market. Investors are typically growth-focused venture capital firms and strategic investors.
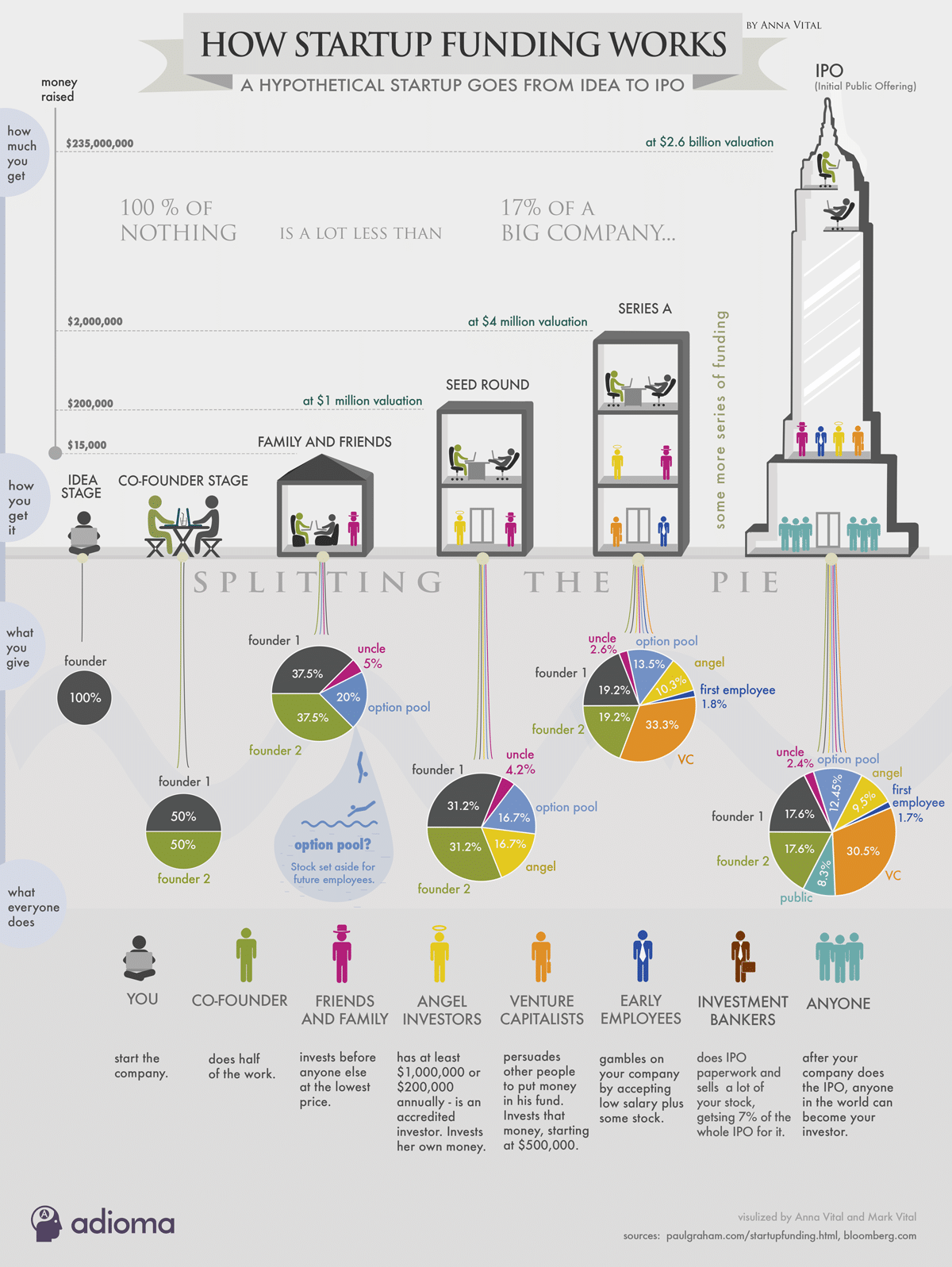
As a startup progresses through these stages, the funding objectives, investors, and goals evolve accordingly, reflecting the company's growth and development. The table below provides an overview of the key aspects that differentiate the Pre-Seed, Seed, and Series stages in startup funding. Each stage serves a specific purpose in a startup's growth journey and involves different funding ranges, investor profiles, and goals.
| Aspect | Pre-Seed Stage | Seed Stage | Series Stage |
| Stage Purpose | - Idea validation and concept exploration. | - Validate concept, build MVP, and initial traction. | - Accelerate growth, expand operations, and prepare for further scaling. |
| Funding Range | - Typically the smallest funding round, ranging from tens of thousands to a few million dollars. | - Smaller than later rounds but larger than Pre-Seed, often ranging from a few hundred thousand to several million dollars. | - Larger funding compared to Seed, often ranging from several million to tens of millions of dollars. |
| Investors | - Friends and family investors, occasionally angel investors. | - Angel investors, early-stage venture capital firms, and occasionally friends and family. | - Established venture capital firms, institutional investors, and sometimes corporate investors. |
| Use of Funds | - Market research, early product development, concept validation. | - Product development, initial marketing efforts, building MVP, and gaining initial traction. | - Marketing expansion, team growth, infrastructure enhancement, market expansion, acquisitions, and scaling operations. |
| Product Development | - Concept validation, early-stage prototypes. | - Building MVP (Minimum Viable Product) and prototypes. | - Optimizing existing product based on user feedback, scaling production, and potentially launching new product lines. |
| Validation | - Business model exploration, market assessment. | - Business model validation, proof of market demand. | - Proven business model, growing customer base, path to profitability, and scalability. |
| Investor Expectations | - High-risk tolerance, early-stage idea exploration. | - Accepts higher risk but expects to see progress and initial market traction. | - Expects strong growth potential, proven business model, and a clear path to profitability. |

